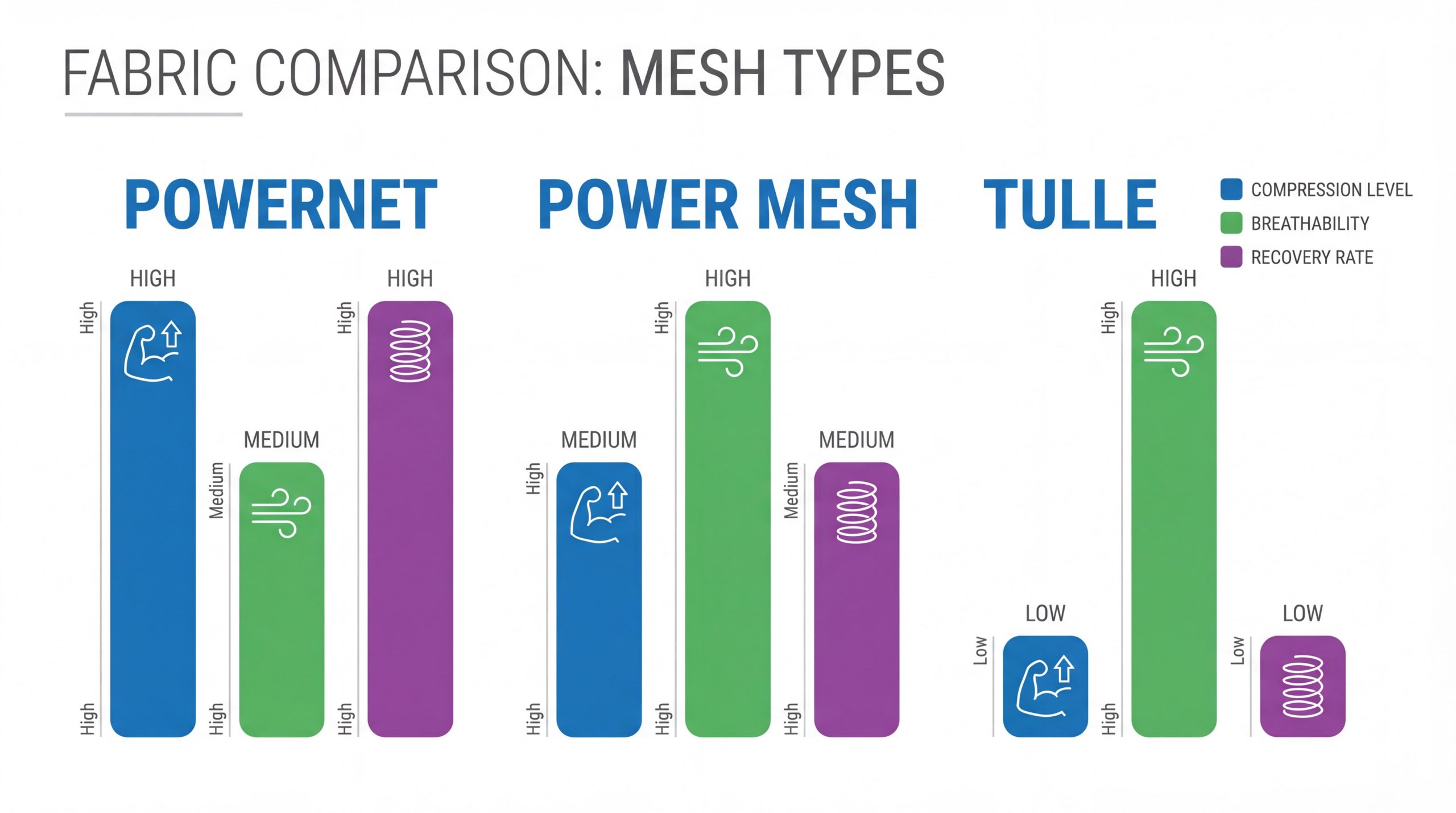
Powernet and power mesh are high-performance synthetic materials designed to provide varying levels of support, compression, and breathability in modern garment construction. Designers and manufacturers often struggle to find materials that offer high-grade compression without sacrificing wearer comfort or causing skin irritation. When you select the wrong material, the result is often “garment fatigue,” where pieces lose their shape and elasticity after just a few wears, leading to high return rates and damaged brand reputation. By understanding the technical nuances of these specialized mesh fabric types , professionals can produce body-sculpting apparel that balances industrial strength with sophisticated aesthetics.
How does powernet differ from other mesh fabric types?
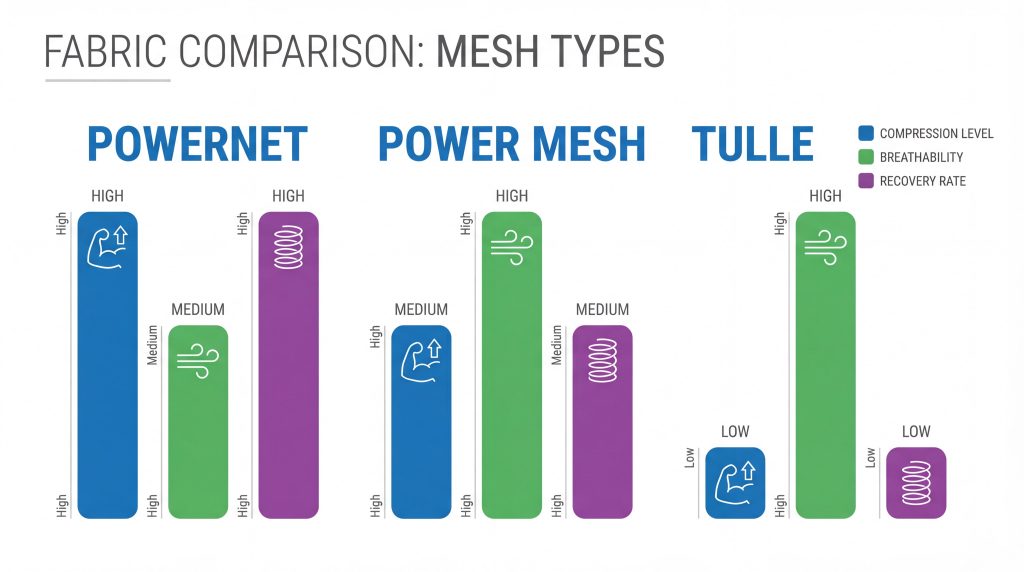
Powernet is distinguished from other mesh fabric types by its hexagonal, reinforced knit structure that provides significantly higher compression and durability. Unlike standard decorative meshes or power-mesh variants, powernet is engineered specifically for functional support in heavy-duty applications like medical-grade shapewear and bra wings.
Defining the Density of Powernet
The density of powernet is determined by its unique warp-knit construction, which involves a complex interlacing of nylon and elastane fibers. This creates a fabric that is not only strong but also remarkably resistant to running or fraying when cut.
Think about it:
- High GSM (Grams per Square Meter) ensures maximum opacity.
- Multi-directional stretch allows for targeted body contouring.
- Reinforced hexagonal cells provide a stable “modulus” of resistance.
Powernet vs. Traditional Tulle
While traditional tulle is primarily aesthetic and prone to tearing under tension, powernet is a structural workhorse designed to withstand constant pressure. It offers a firm hand-feel that maintains its integrity over hundreds of wash cycles.
But here is the kicker: Powernet can be layered to create “zones” of compression, allowing designers to vary the level of support within a single garment without adding excessive bulk. This versatility makes it the gold standard for high-performance foundation garments.
Key TakeawayPowernet serves as the foundational material for high-compression garments, offering a hexagonal knit that provides unparalleled structural integrity compared to lighter decorative alternatives.
| Feature | Powernet Specification | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Content | 75-80% Nylon, 20-25% Spandex | Superior recovery and strength | |
| Knit Type | Warp-Knit (Hexagonal) | Run-resistant and durable | |
| Compression | High to Ultra-High | Maximum body sculpting power |
This technical breakdown illustrates why powernet remains the preferred choice for industrial-strength shaping applications where fabric failure is not an option.
What makes power mesh unique among mesh fabric types?
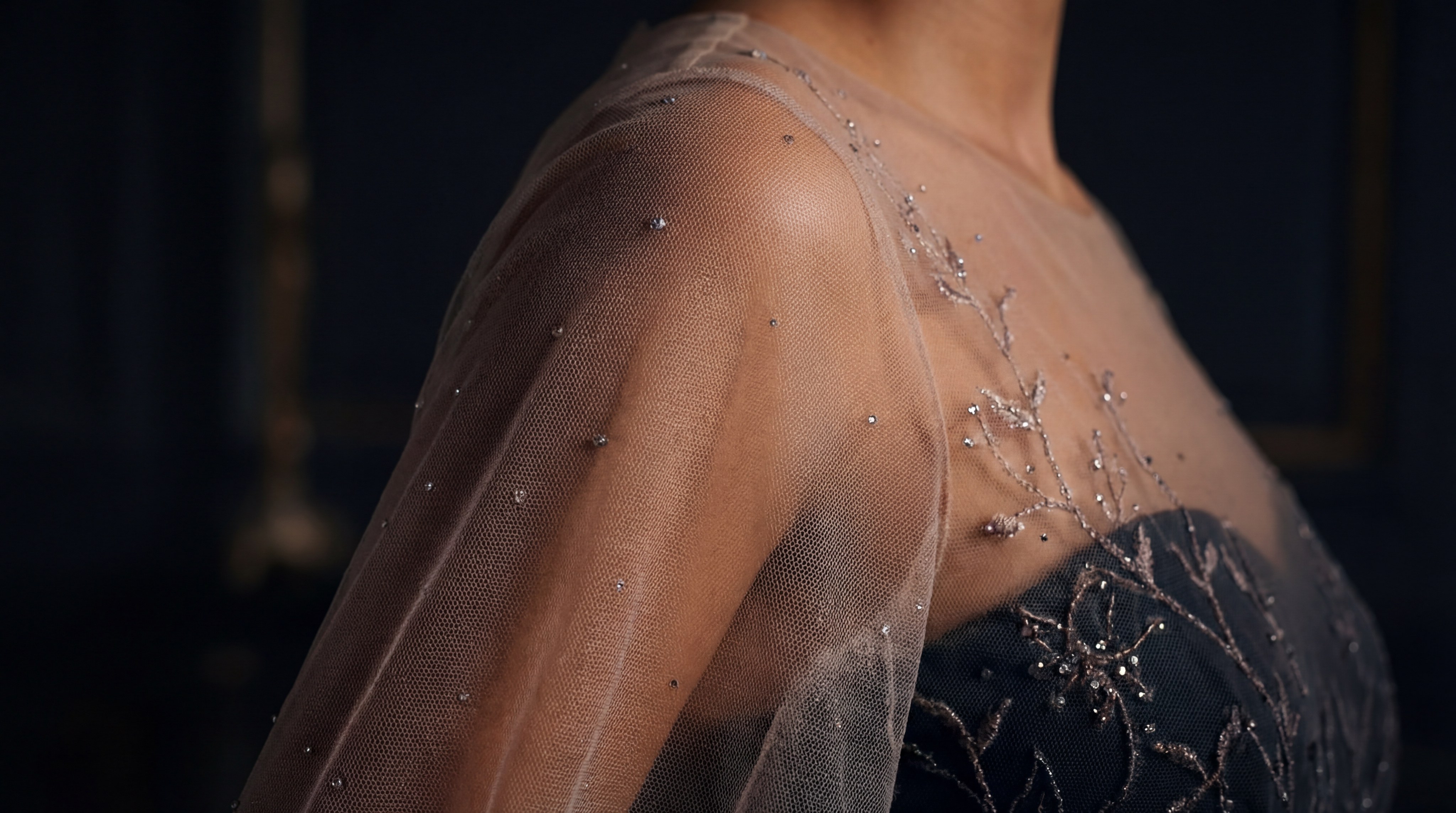

Power mesh is unique among mesh fabric types because it offers a softer drape and greater flexibility, making it ideal for linings and lightweight activewear inserts. While it shares a similar synthetic composition with powernet, its knit is less dense, providing a “second-skin” feel that prioritizes comfort over extreme compression.
The Softness and Drape of Power Mesh
The primary appeal of power mesh lies in its ability to move fluidly with the body, which is essential for performance sports and contemporary fashion. It lacks the rigidity of heavier powernet, allowing it to be used in gathered or ruched designs without creating stiff silhouettes.
You might be wondering:
- Is it breathable enough for high-intensity training?
- Does it provide enough support for athletic linings?
- Can it be used for sheer fashion panels?
Power Mesh as a Versatile Lining
In the world of professional apparel, power mesh is the go-to choice for lining close-fitting dresses and skirts to provide a smooth, line-free finish. It effectively bridges the gap between decorative sheer fabrics and heavy-duty shapewear materials.
The reality is: Manufacturers use power mesh to add a layer of modesty and slight smoothing to garments that require a high degree of stretch. Its fine gauge ensures that it remains invisible under outer fabrics while providing a comfortable barrier against the skin.
Key TakeawayPower mesh is the versatile, lightweight cousin of powernet, offering excellent drape and moisture-wicking properties for activewear and garment linings.
| Attribute | Power Mesh Characteristic | Ideal Use Case | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hand-feel | Soft and silky | Intimate apparel linings | |
| Stretch | High four-way stretch | Activewear panels | |
| Transparency | Semi-sheer | Illusion necklines |
The balance of softness and elasticity makes power mesh an indispensable tool for designers who need functional performance without industrial stiffness.
How does warp knitting define these mesh fabric types?
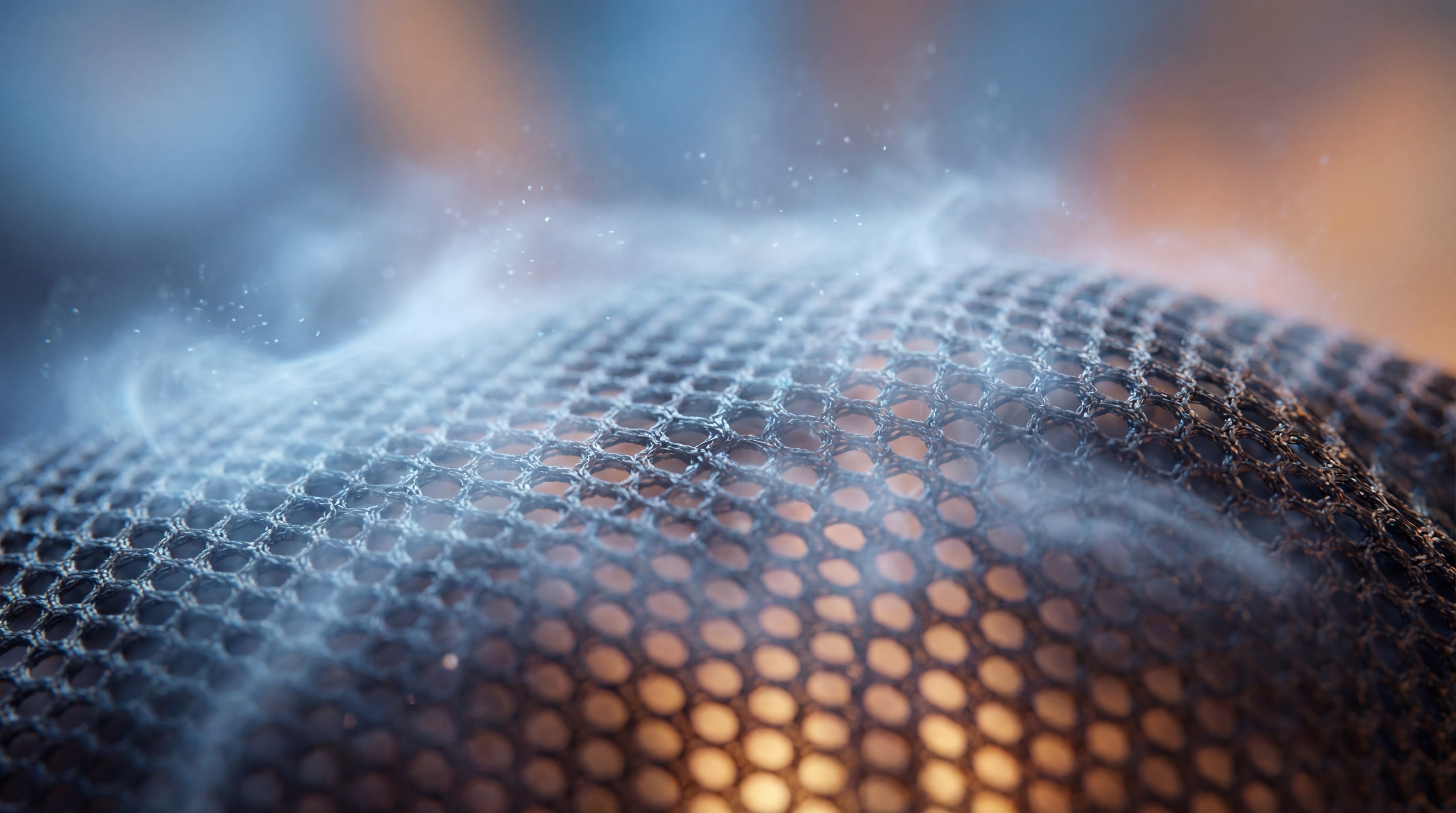

The warp knitting process defines these mesh fabric types by creating a series of interlocking loops that run vertically, resulting in a stable material that does not unravel. This specialized manufacturing technique, often used for stretch-fabric production, allows for precise control over the fabric’s elasticity and recovery rates.
The Mechanics of Warp Knitting
In warp knitting, thousands of individual yarns are fed into the machine simultaneously, creating a complex web of loops that are far more stable than traditional weft-knit fabrics. This stability is what allows powernet and power mesh to maintain their shape even under significant tension.
Make no mistake:
- Warp knits are inherently run-resistant.
- They allow for the integration of high spandex percentages.
- The process produces a clean, professional finish on both sides.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Elongation
A defining characteristic of these fabrics is the difference in stretch between the length (warp) and width (weft) of the material. Most high-quality technical meshes are engineered to have a specific “power” direction, which designers must identify during the cutting phase.
Think about it: If the fabric is cut in the wrong direction, the garment will fail to provide the intended support. Professionals always test the modulus of the stretch to ensure the greatest resistance wraps around the body’s circumference.
Key TakeawayWarp-knit construction is the secret behind the durability and run-resistance of technical meshes, providing the mechanical stability required for high-tension applications.
| Knitting Factor | Impact on Fabric | Professional Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Loops | Directional stability | Precise support mapping | |
| Parallel Yarns | Increased tensile strength | Resistance to tearing | |
| Loop Interlocking | High recovery rate | Long-term shape retention |
Understanding the geometry of warp knitting is essential for any manufacturer looking to optimize the performance of their technical apparel collections.
What are the best mesh fabric types for body sculpting?
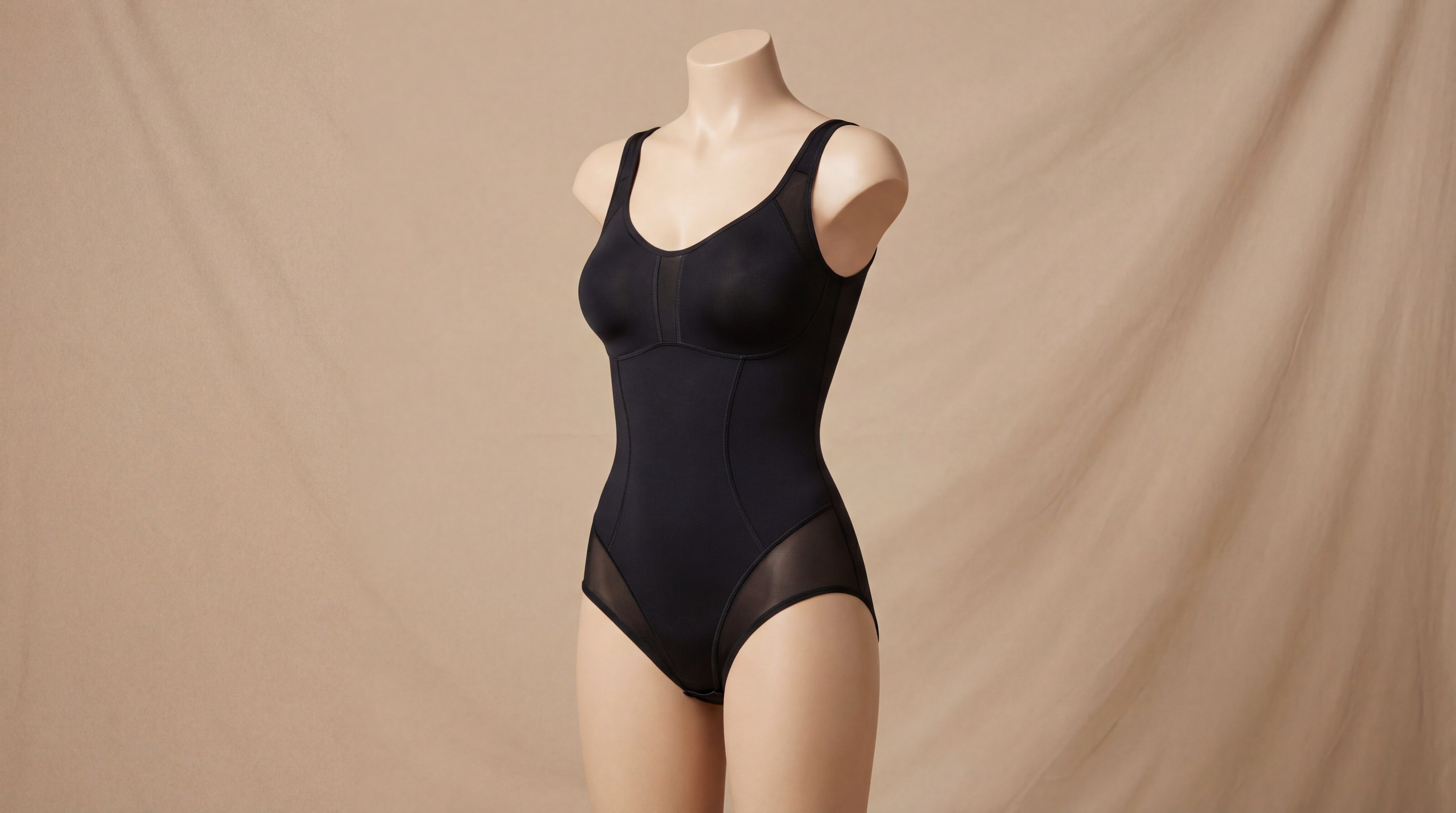

The best mesh fabric types for body sculpting are high-GSM powernets that contain a minimum of 20% spandex for maximum recovery and control. These materials are specifically engineered to apply uniform pressure across the body, smoothing out contours while remaining flexible enough for daily wear.
The Science of Fabric Recovery
Recovery refers to a fabric’s ability to return to its original dimensions after being stretched, and it is the most critical metric for sculpting garments. Fabrics with poor recovery will “bag out” over time, rendering the shapewear ineffective and frustrating the end consumer.
But here is the kicker: High-performance powernet uses heat-set spandex fibers that retain their “memory” far longer than standard elastics. This ensures that a waist cincher or thigh slimmer provides the same level of compression after fifty washes as it did on day one.
Engineering Targeted Support Panels
Strategic paneling allows designers to use different weights of technical mesh to address specific anatomical needs. For instance, a double layer of heavy powernet might be used for tummy control, while a single layer of power mesh is used over the hips for comfort.
It’s a simple fact:
- Reinforced panels prevent rolling and bunching.
- Graduated compression improves circulation and comfort.
- Bonded seams can enhance the sculpting effect without adding bulk.
Key TakeawayFor effective body sculpting, manufacturers must prioritize high-recovery powernet with significant spandex content to ensure long-lasting compression and wearer satisfaction.
| Compression Level | GSM Range | Primary Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light | 100 – 150 | Smoothing linings | |
| Medium | 150 – 220 | Post-surgical support | |
| Firm | 220 – 300+ | High-performance shapewear |
Selecting the correct weight and recovery profile is the difference between a garment that merely fits and one that truly transforms the silhouette.
Which mesh fabric types suit intimate apparel best?
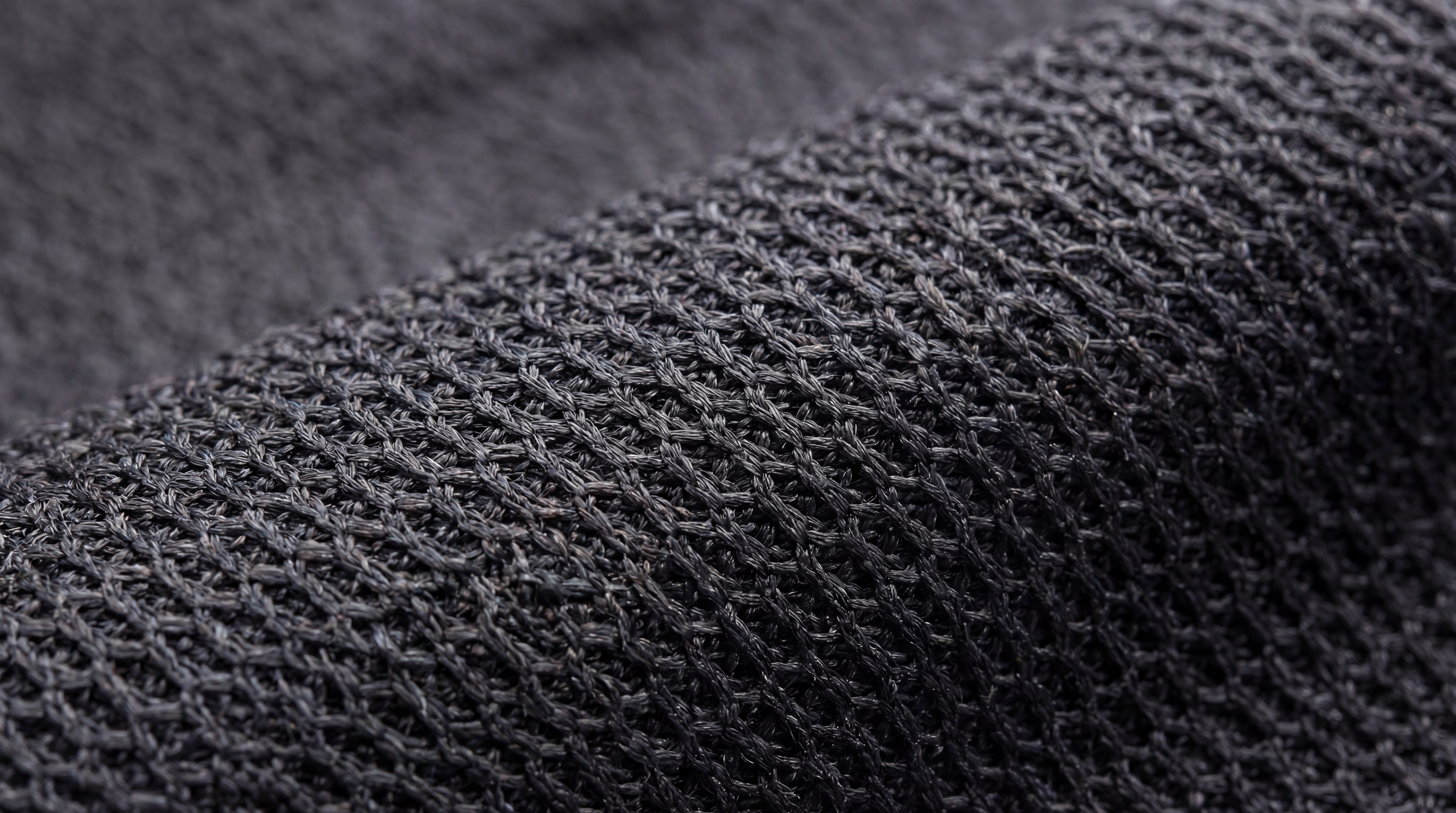

Intimate apparel requires a delicate balance of different mesh fabric types, using high-modulus powernet for bra bands and softer power mesh for cup linings or decorative elements. While powernet provides the necessary structural support, materials like glitter tulle can be layered over them to add aesthetic appeal without compromising function.
Lingerie Construction: Wings and Bridges
The “wing” of a bra is the most hardworking part of the garment, responsible for 80% of the support, and it almost exclusively utilizes powernet. The bridge, or the center front, also requires a stable material to keep the cups positioned correctly against the chest wall.
Think about it:
- Powernet prevents the band from riding up during movement.
- It provides a smooth back silhouette by containing soft tissue.
- The open knit allows for skin breathability under tight elastics.
Comfort and Skin-Friendly Finishes
Because lingerie is worn directly against the skin for extended periods, the “hand” or softness of the mesh is paramount. Modern manufacturers often apply silicone or brushed finishes to technical meshes to prevent the chafing commonly associated with cheaper synthetic fibers.
The reality is: Premium intimate brands invest in nylon-based powernets because they offer a silkier feel compared to polyester alternatives. This ensures that even high-compression pieces remain comfortable enough for all-day wear in sensitive areas.
Key TakeawaySuccessful lingerie design relies on a hybrid approach, combining the industrial strength of powernet in support zones with the skin-friendly softness of power mesh.
| Component | Recommended Mesh Type | Priority | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bra Band (Wings) | Heavy Powernet | Modulus/Support | |
| Cup Lining | Fine Power Mesh | Softness/Comfort | |
| Side Panels | Medium Powernet | Smoothing/Stability |
Choosing the right mesh for each specific component of a bra ensures a product that offers both technical performance and luxurious comfort.
How do designers use mesh fabric types for sheer overlays?

Designers utilize various mesh fabric types for sheer overlays to create visual depth, illusion necklines, and textured effects that maintain a garment’s structural integrity. Stretch meshes are particularly favored for their ability to cling to the body’s curves, providing a “naked” look while offering a supportive base for embellishments.
Creating Illusion Necklines and Sleeves
The “illusion” effect is achieved by using a fine-gauge power mesh that closely matches the wearer’s skin tone, making the fabric virtually disappear from a distance. This allows for the placement of heavy lace or beadwork on what appears to be bare skin.
But here is the kicker: Because the mesh is a warp-knit, it can support the weight of dense embroidery without sagging or tearing. This technical capability has revolutionized bridal and eveningwear design, allowing for more daring and intricate silhouettes.
Achieving the Ruched Effect
Ruching involves gathering fabric along a seam to create flattering folds, and power mesh is the ideal candidate for this technique due to its superior drape. It compresses the body slightly while the folds of fabric provide camouflaging texture over areas of concern.
Make no mistake:
- Ruched power mesh hides seam lines and body imperfections.
- It adds a high-fashion, three-dimensional quality to simple designs.
- The stretch ensures the gathers stay in place during movement.
Key TakeawayMesh overlays provide a unique combination of aesthetic transparency and functional support, making them a staple in high-end fashion and bridal design.
| Application | Mesh Type | Aesthetic Goal | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Illusion Panels | Micro-Power Mesh | Invisibility and support | |
| Gathered Sleeves | Soft Stretch Mesh | Volume and movement | |
| Texture Overlays | Patterned Mesh | Visual depth |
By mastering the use of sheer technical fabrics, designers can create garments that appear fragile and ethereal while remaining durable and supportive.
Which mesh fabric types offer long-term durability?

Long-term durability in mesh fabric types is primarily found in nylon-based blends that have been treated for UV and chemical resistance. For specialized industrial or safety applications, manufacturers often turn to flame retardant mesh to ensure the fabric meets strict regulatory standards without losing its elastic properties.
Fiber Composition: Nylon vs. Polyester
While both fibers are common, nylon-based meshes generally offer superior abrasion resistance and a higher recovery rate than polyester. Polyester is often chosen for its colorfastness and lower cost, but it can feel “crunchy” and lose its stretch more quickly under stress.
Think about it:
- Nylon is more resilient against the friction of daily wear.
- It dyes more deeply, resulting in richer, more vibrant colors.
- Polyester is better suited for garments exposed to heavy chlorine.
Preventing Fabric Fatigue Over Time
Fabric fatigue occurs when the elastane fibers within the mesh break down due to heat, chemicals, or over-extension. Using high-quality “branded” spandex and proper finishing techniques can significantly extend the lifespan of a technical mesh garment.
The reality is: Businesses that cut corners on mesh quality often face a “delayed” penalty in the form of customer dissatisfaction months after the purchase. Durable mesh maintains its “modulus”—the force required to stretch it—over hundreds of wear cycles.
Key TakeawayDurability in technical mesh is a product of high-quality base fibers and advanced finishing processes that protect the elastic core from degradation.
| Fiber Property | Nylon Mesh | Polyester Mesh | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Good | |
| Elastic Recovery | High | Moderate | |
| Heat Sensitivity | Higher (Melt risk) | Lower |
Investing in high-durability mesh types reduces long-term costs by minimizing returns and building consumer trust in the brand’s quality.
How does breathability vary across mesh fabric types?

Breathability varies across mesh fabric types based on the “openness” of the knit and the moisture-wicking properties of the synthetic yarns used. Despite their tight compression, high-quality powernets are engineered with an open-cell structure that allows for significant airflow and thermoregulation.
Moisture-Wicking and Thermoregulation
In activewear and shapewear, the ability to move sweat away from the skin is just as important as the fabric’s stretch. Technical meshes use capillary action to pull moisture through the fibers to the surface of the fabric, where it can evaporate quickly.
But here is the kicker:
- Breathable mesh prevents the “sauna effect” common in cheap shapewear.
- It helps maintain a stable body temperature during intense activity.
- Open-knit structures reduce the risk of skin rashes and bacterial growth.
Safety and Compliance in Technical Meshes
For professional uniforms and protective gear, breathability must be balanced with safety requirements such as flame resistance or high-visibility. These technical meshes must undergo rigorous testing to ensure they provide airflow without compromising the protective barrier.
The reality is: Modern industrial meshes can achieve high levels of airflow while still providing the tensile strength needed for load-bearing vests or safety harnesses. This intersection of comfort and safety is a hallmark of advanced textile engineering.
Key TakeawayThe open-cell geometry of powernet and power mesh ensures that even high-compression garments remain breathable and comfortable in demanding environments.
| Mesh Type | Air Permeability | Best Environment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fine Power Mesh | High | Summer activewear | |
| Standard Powernet | Moderate | All-day shapewear | |
| Heavy Powernet | Low to Moderate | Medical support |
Effective thermoregulation is a critical selling point for premium technical apparel, as it directly impacts the wearer’s comfort and performance.
What techniques work for sewing these mesh fabric types?

Sewing these mesh fabric types requires specialized tools like ballpoint needles and walking feet to prevent skipped stitches and fabric damage. Professionals often refer to industry blogs for the latest tips on handling high-stretch materials to ensure clean, durable seams that can withstand the garment’s compression forces.
Choosing the Correct Needle and Thread
Standard sharp needles can pierce and break the delicate knitted loops of mesh fabric, leading to holes and “runs.” Ballpoint or stretch needles are essential as they have a rounded tip that slides between the fibers rather than cutting through them.
Think about it:
- Polyester thread is preferred for its strength and lack of shrinkage.
- Wooly nylon thread in the bobbin or looper adds extra softness.
- A narrow zigzag or serged stitch is necessary to allow for stretch.
Managing Tension and Seam Popping
The most common failure in mesh garments is “seam popping,” where the thread breaks because it cannot stretch as far as the fabric. Using a walking foot helps feed the slippery mesh evenly through the machine, preventing the fabric from stretching out of shape during the sewing process.
But here is the kicker: Basting seams with a long straight stitch before final assembly can save hours of unpicking and prevent permanent damage to the mesh. This allows for fit adjustments while the delicate fibers are still relatively undisturbed.
Key TakeawayProfessional results with technical mesh depend on using the right needles, specialized feet, and elastic stitch patterns that mirror the fabric’s natural elongation.
| Tool/Setting | Recommendation | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Needle Type | 75/11 Stretch or Ballpoint | Prevent fiber breakage | |
| Stitch Type | 3-Step Zigzag or 4-Thread Overlock | Allow for maximum stretch | |
| Presser Foot | Walking Foot or Teflon Foot | Even fabric feeding |
By adopting these specialized sewing techniques, manufacturers can ensure that their garments are as durable at the seams as they are in the fabric body.
How do you choose between these mesh fabric types?

Choosing between different mesh fabric types depends on the desired balance of compression, drape, and skin-feel required for the specific end-use. A manufacturer must evaluate technical specifications like GSM and modulus to determine if a material will meet the performance expectations of their target market.
Evaluating Weight and Stretch Percentage
The weight of the fabric (GSM) is the most reliable indicator of its compression level, with heavier weights generally offering more “hold.” However, the stretch percentage must also be considered, as a fabric that is too tight may be impossible for the consumer to put on.
You might be wondering:
- Should I prioritize 4-way stretch or 2-way stretch?
- Is the “hand-feel” soft enough for my luxury brand?
- Does the price point allow for nylon-based premium mesh?
Sourcing Strategy for Scale
For large-scale production, consistency is the most important factor when selecting a mesh supplier. Variations in the elastane content or the heat-setting process between batches can lead to significant sizing issues in the finished garments.
The reality is: Successful brands always request physical swatches and perform “wash and wear” tests before committing to bulk orders. This hands-on evaluation is the only way to truly understand how a mesh will behave in a real-world environment.
Key TakeawayThe selection process for technical mesh must be data-driven, prioritizing recovery rates and batch consistency to ensure a high-quality finished product.
| Decision Factor | Powernet Priority | Power Mesh Priority | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximum Compression | Comfort and Drape | |
| Layering | Often used as a base | Often used as a lining | |
| Cost | Higher (due to density) | Lower (lighter weight) |
By carefully weighing these factors, designers can select the optimal mesh fabric types to bring their technical visions to life.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct roles of powernet and power mesh allows manufacturers to solve the age-old problem of balancing body-sculpting power with all-day wearer comfort. By selecting high-recovery mesh fabric types, you eliminate the risks of garment fatigue and skin irritation that often plague lower-quality collections. Whether you are constructing high-performance activewear, medical-grade shapewear, or delicate intimate apparel, the right technical mesh provides the foundation for success. Don’t let inferior materials compromise your brand’s reputation for quality and durability. To explore our full range of professional textiles or to request specific swatches for your next project, contact us today and let our experts help you find the perfect fit.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use power mesh as a substitute for powernet in a bra band?No, because power mesh typically lacks the high modulus (resistance) required to support larger bust sizes effectively; powernet is necessary for structural components.
What’s the best way to prevent mesh from curling during cutting?Using a rotary cutter is the most effective method, as it provides consistent downward pressure and prevents the shifting that occurs with traditional shears.
Can I wash garments made from powernet in a regular washing machine?Yes, but only if you use a mesh laundry bag and cold water to protect the spandex fibers from heat and agitation.
How do I identify the “power” direction of the stretch?Simply pull the fabric in both directions; the direction that offers the most resistance (the “snap back”) is the one that should wrap around the body.
What’s the best thread to use for high-compression mesh seams?Polyester thread is the ideal choice due to its high tensile strength and resistance to chemicals and UV degradation.