
Mesh and netting fabrics are open-weave textiles characterized by their breathable, porous structures and diverse applications across high-performance industries. Many designers and engineers struggle to identify which specific mesh fabric types provide the necessary tensile strength or UV resistance for their unique commercial projects. Selecting the incorrect material can lead to catastrophic product failure or safety hazards in specialized environments. This guide provides the technical clarity needed to navigate the vast array of mesh fabric types available today, ensuring optimal material selection for any performance requirement.
What are the primary mesh fabric types?

The primary mesh fabric types include polyester, nylon, and spandex-blended knits, each defined by their unique hole size, weight, and structural stability. Understanding these nylon mesh fabric variations is essential because the base polymer dictates how the material will respond to environmental stressors.
Identifying Fundamental Synthetic Categories
Think about it: not all mesh is created equal in industrial settings.
- Synthetic Foundations: Most modern mesh is crafted from polyester or nylon for maximum durability.
- Knit Structures: Fabrics are typically warp-knitted to prevent fraying when the material is cut.
- Specialized Finishes: Antimicrobial and moisture-wicking treatments are common performance additions.
Key Takeaway: The foundation of mesh selection rests on identifying whether your application requires the rigidity of polyester or the elasticity of a nylon blend.
| Mesh Category | Primary Material | Primary Characteristic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rigid Mesh | Polyester / Nylon | High structural stability | |
| Elastic Mesh | Nylon / Spandex | Superior body-contouring | |
| Industrial Mesh | Heavy-duty Poly | Extreme tear resistance |
This classification system allows users to narrow down material choices based on the mechanical demands of the final product.
How do mesh fabric types differ from netting?
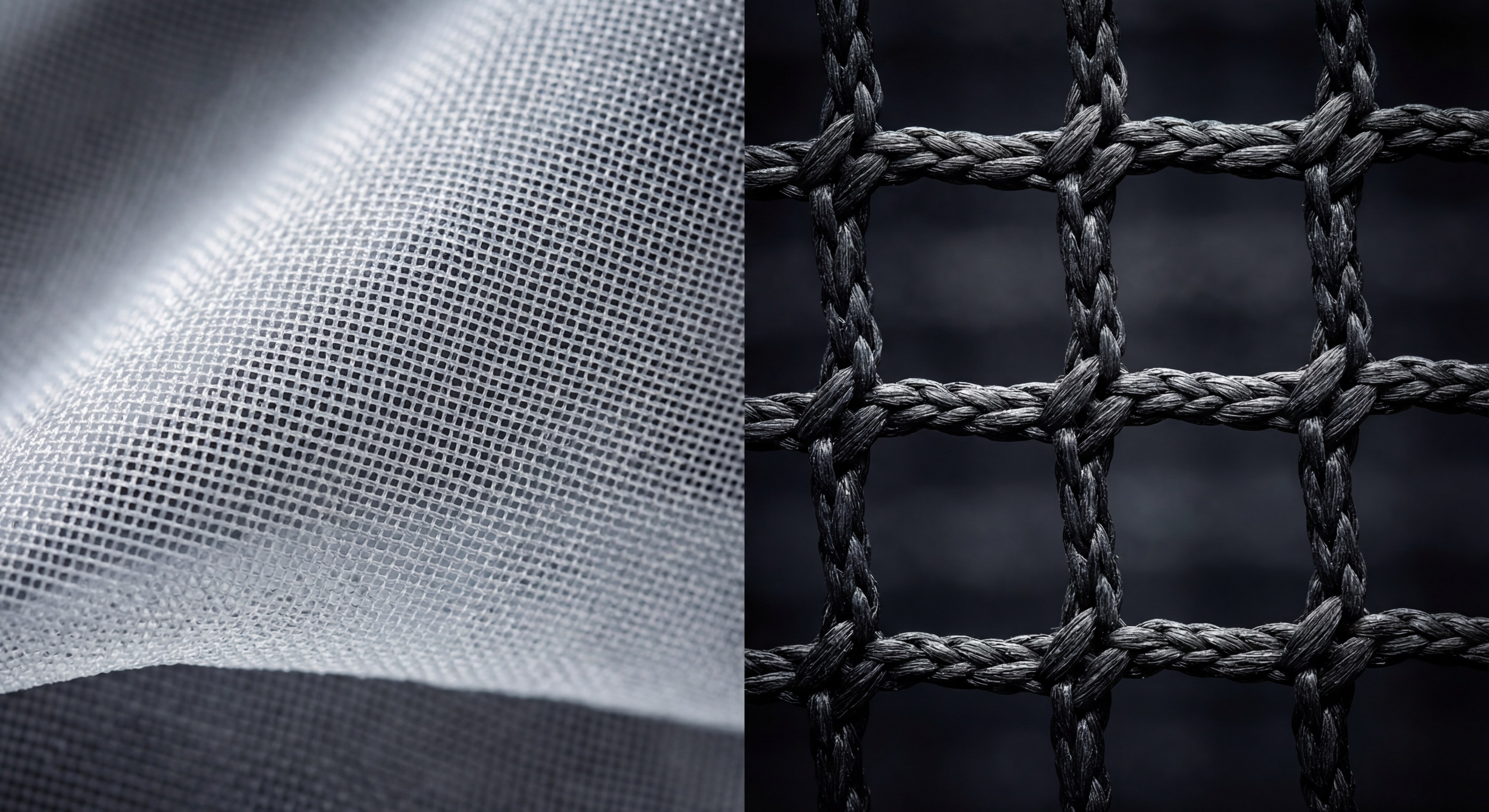

Mesh fabric types are generally distinguished from netting by their hole density and the complexity of their specific knit pattern. While the terms are often used interchangeably, identifying the structural differences between these mesh fabric types is crucial for determining the level of breathability and visibility required for your project.
Structural Variations in Textile Weave
Here is the kicker:
- Mesh Density: Mesh typically features smaller, more frequent openings for a smoother surface.
- Netting Openness: Netting has larger, more distinct gaps designed for maximum transparency.
- Surface Texture: Mesh often feels significantly softer against the skin compared to coarser industrial netting.
Key Takeaway: Netting is preferred for maximum airflow and containment, while mesh provides a more balanced surface for apparel comfort and printing.
| Feature | Mesh Fabric | Netting | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hole Size | Fine to Medium | Large and Defined | |
| Transparency | Translucent | High Visibility | |
| Common Use | Athletic Linings | Cargo Containment |
Comparing these two structures reveals why mesh is more suitable for intimate apparel while netting excels in heavy-duty containment applications.
Which mesh fabric types offer the best stretch?
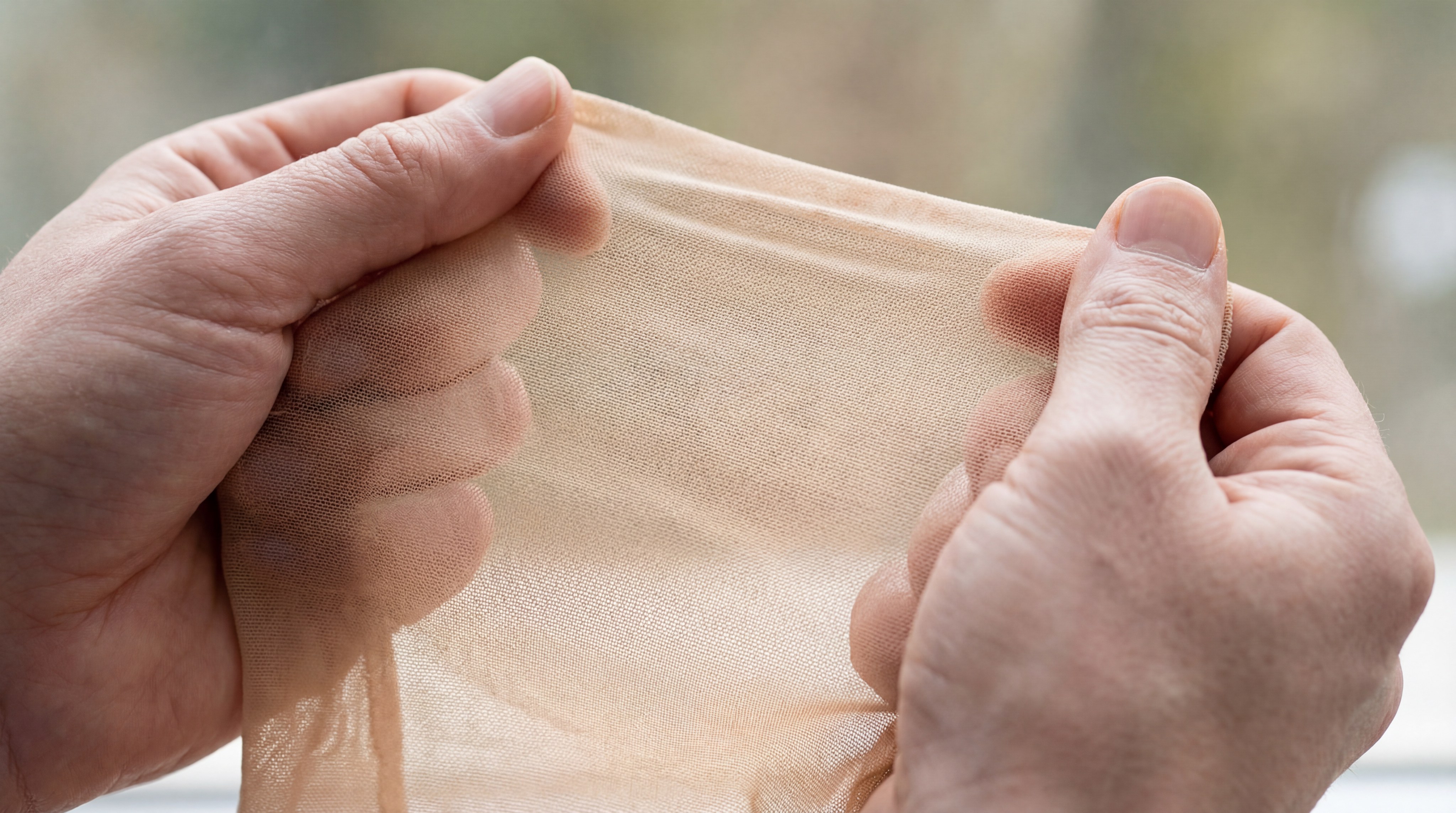

The best stretch is found in elastomeric mesh fabric types like power mesh , which are engineered with a high percentage of spandex to provide four-way recovery. These specialized mesh fabric types are essential for garments that must maintain their shape while under constant tension.
The Power of Elastomeric Fibers
The best part? You do not have to sacrifice breathability to achieve high-performance compression.
- Four-Way Stretch: These fabrics expand both horizontally and vertically for total movement.
- Compression Ratings: Different weights offer varying levels of body-sculpting or medical support.
- Soft Touch: High-quality elastomeric mesh is designed to be non-irritating during prolonged wear.
Key Takeaway: For shapewear, medical braces, or athletic compression, a nylon-spandex blend is the industry standard for performance recovery.
| Stretch Type | Fiber Blend | Best Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Mesh | Nylon / Spandex | Shapewear and Bras | |
| Athletic Mesh | Polyester / Spandex | Performance Leggings | |
| Micro Mesh | Fine Nylon / Elastane | Lingerie Linings |
Selecting the correct elastomeric blend ensures the final garment maintains its integrity even after repeated laundering cycles.
Are there specific mesh fabric types for clothing?

Yes, there are several specialized clothing-grade mesh fabric types, including bird’s eye, jersey, and tricot mesh, designed for skin-contact comfort. These mesh fabric types are optimized for wearability, focusing on moisture-wicking properties and a soft hand-feel to prevent chafing.
Subcategories of High-Performance Apparel Mesh
Now: let us look at the specific apparel subcategories.
- Jersey Mesh: Features larger holes for maximum ventilation during high-impact sports activities.
- Bird’s Eye Mesh: A textured knit that mimics a bird’s eye, popular for professional polo shirts.
- Tricot Mesh: A run-resistant warp knit often utilized as a lining for swimwear and jackets.
Key Takeaway: When designing apparel, the choice of mesh depends on whether the fabric serves as an outer layer or a functional lining.
| Apparel Mesh | Key Benefit | Typical Garment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tricot | Soft/Lightweight | Jacket Linings | |
| Bird’s Eye | Pro Appearance | Team Uniforms | |
| Jersey | High Airflow | Sports Jerseys |
Identifying the specific apparel subcategory ensures the final garment meets both aesthetic standards and performance requirements.
What mesh fabric types work best for heavy bags?

For luggage and equipment, the most effective mesh fabric types are bag and luggage mesh made from heavy-duty polyester with high denier counts. These mesh fabric types are engineered to support significant weight without tearing or sagging under industrial loads.
Durability Factors for Bags and Luggage
But that’s not all.
- Reinforced Edges: These fabrics are designed to be integrated into heavy structural seams.
- Abrasion Resistance: This is necessary for bags that will endure rough handling or dragging.
- PVC Coatings: Some bag meshes are coated for additional rigidity and water resistance.
Key Takeaway: The strength of a bag mesh is measured by its burst strength, making polyester the preferred choice for industrial bags.
| Bag Mesh Type | Material | Use Case | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Square | 500D+ Polyester | Equipment Bags | |
| Pocket Mesh | Medium Nylon | Backpack Side Pockets | |
| Coated Mesh | PVC / Poly | Industrial Filter Bags |
High-denier polyester mesh provides the necessary structural integrity for products that must survive abrasive environments.
Can outdoor mesh fabric types withstand the sun?

Outdoor mesh fabric types are specially treated with UV inhibitors to prevent degradation and fading when exposed to direct solar radiation. Without these treatments, standard mesh fabric types would become brittle and lose their tensile strength within a single season of use.
Weatherproofing and External Protection
Why does this matter?
- UV Stabilization: This prevents the polymer chains from breaking down under intense sunlight.
- Mildew Resistance: Synthetic fibers like polyester naturally resist mold and mildew growth.
- Hydrophobic Properties: Designed to shed water quickly to prevent sagging or weight gain.
Key Takeaway: Outdoor mesh is essential for fencing, pool covers, and marine seating where environmental exposure is constant.
| Outdoor Variant | Primary Protection | Common Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Screen | Heat/UV Blockage | Patio Shades | |
| Marine Mesh | Salt/UV Resistance | Boat Seating | |
| Safety Fencing | Weather Resistance | Construction Barriers |
The integration of UV-resistant chemistry ensures that the mesh remains functional and vibrant despite harsh outdoor conditions.
Which mesh fabric types ensure industrial safety?
Industrial safety is addressed by specialized flame retardant mesh fabric types that include high-visibility dyes and protective finishes. These mesh fabric types must meet strict regulatory standards to be utilized in public spaces or hazardous work environments.
Safety Standards and Specifications
Look at the data:
- Flame Retardancy: Fibers are either inherently flame-retardant or treated with specialized chemical coatings.
- ANSI Compliance: High-visibility mesh is utilized for safety vests in aviation and construction.
- Static Dissipation: Some industrial meshes include carbon fibers to prevent dangerous electrical discharge.
Key Takeaway: Using certified FR mesh is a legal requirement for trade show displays and protective gear in most regions.
| Safety Mesh | Certification | Usage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR Mesh | NFPA 701 | Tents and Displays | |
| Hi-Vis Mesh | ANSI/ISEA 107 | Traffic Safety Vests | |
| Cut-Resistant | EN 388 | Protective Sleeves |
Adhering to safety certifications when selecting mesh ensures compliance with international protection standards and minimizes project liability.
How are various mesh fabric types manufactured?
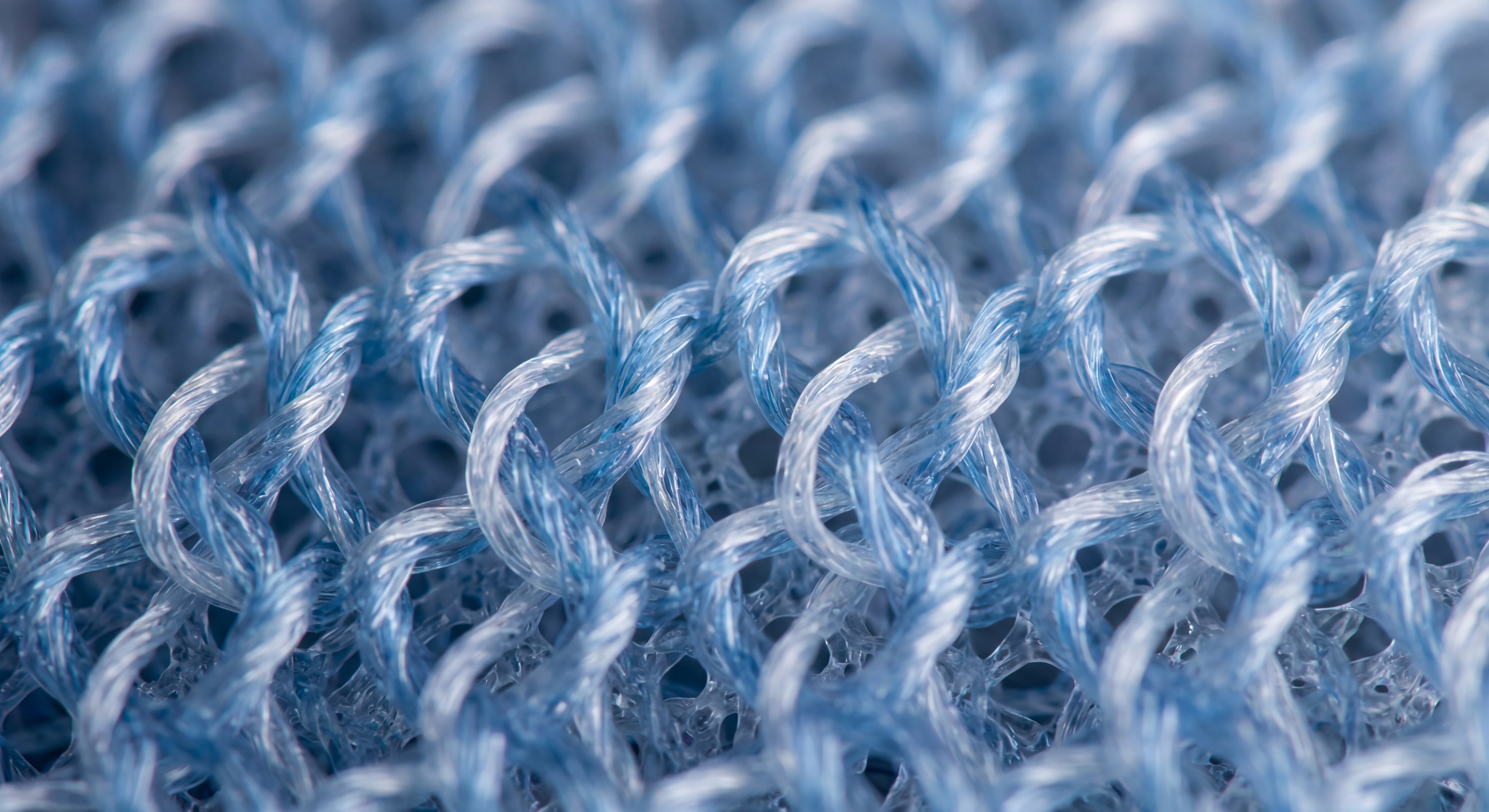

Most modern mesh fabric types are manufactured using warp-knitting technology on Raschel or Tricot machines for superior stability. This manufacturing process defines the hole geometry of different mesh fabric types, allowing for intricate patterns that traditional weaving cannot achieve.
The Warp Knitting Process
Here is how it works:
- Vertical Yarn Supply: Unlike weft knitting, warp yarns run parallel to the fabric length.
- Loop Interlocking: Machines create zig-zag patterns that lock fibers firmly in place.
- Stability: Warp knits are remarkably stable and will not unravel if a single thread is cut.
Key Takeaway: The manufacturing method determines whether a mesh is run-proof, which is critical for high-performance applications.
| Machine Type | Resulting Fabric | Structural Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raschel | Heavy Mesh | Complex shapes and strength | |
| Tricot | Fine Mesh | Elasticity and softness | |
| Circular Knit | Tubular Mesh | Seamless construction |
Understanding the machinery behind the textile allows engineers to specify the exact knit construction needed for mechanical requirements.
Why choose specific mesh fabric types for footwear?
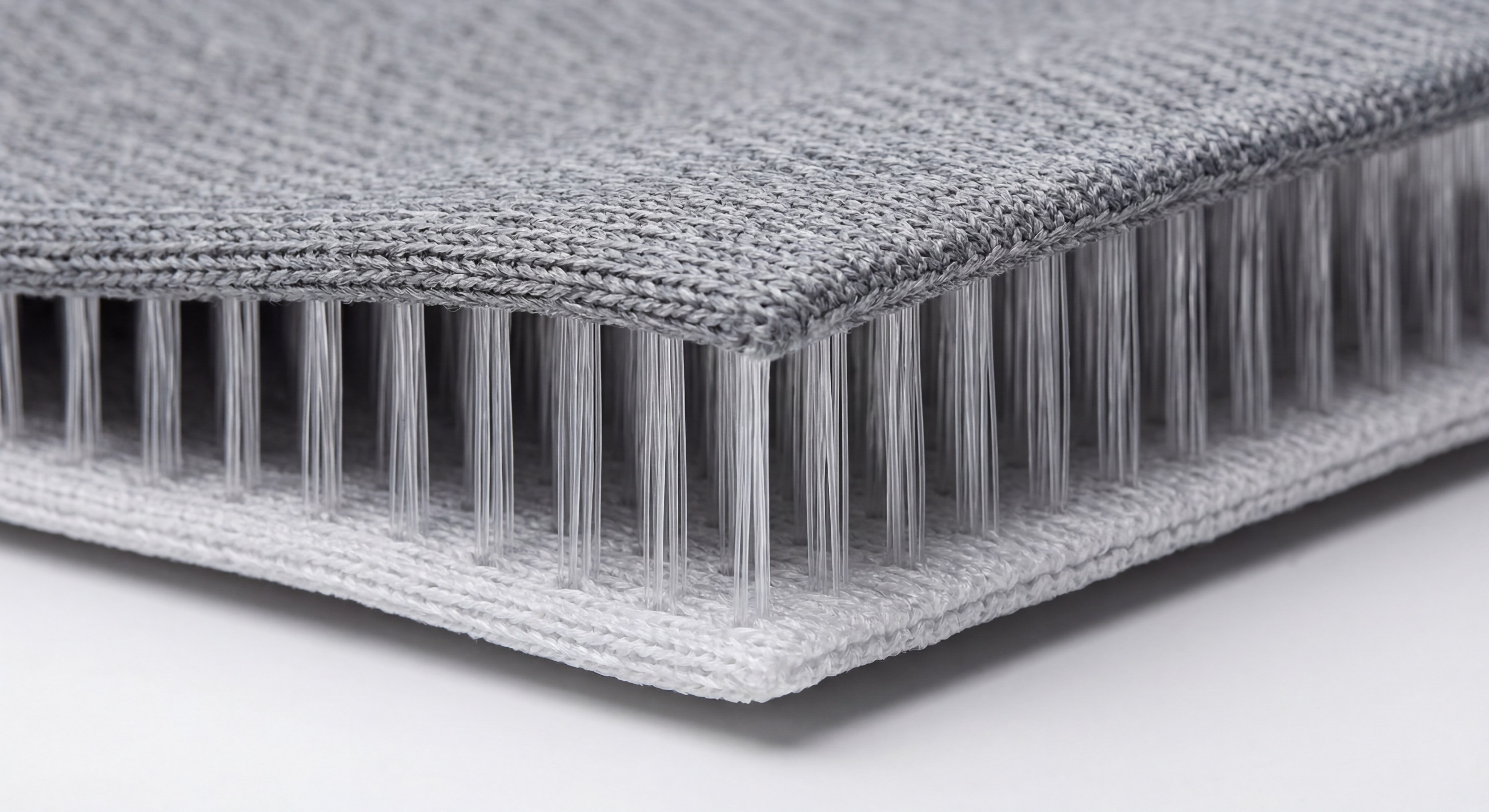

Footwear designers choose specialized mesh fabric types like 3D spacer mesh to provide essential cushioning and moisture management for athletes. These mesh fabric types are unique because they consist of two separate fabric layers joined by a vertical spacer yarn.
The Advantage of Spacer Mesh
It gets better:
- Compression Recovery: The vertical yarns act like tiny springs to absorb impact.
- Airflow Channels: The 3D structure allows heat to escape the shoe upper easily.
- Weight Reduction: Mesh uppers significantly reduce the overall weight of performance footwear.
Key Takeaway: Spacer mesh has revolutionized the sneaker industry by providing a lightweight, breathable alternative to solid materials.
| Footwear Mesh | Feature | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Spacer | Triple Layer | Impact Absorption | |
| Engineered Mesh | Zoned Knitting | Targeted Support | |
| Sandwiched | Breathable Layers | Internal Comfort |
The transition to mesh uppers has enabled the creation of high-performance footwear that prioritizes both speed and long-term comfort.
Where can I find specialized mesh fabric types?

Specialized mesh fabric types can be sourced through industrial textile manufacturers who offer custom finishing and application-driven design services. Finding the right mesh fabric types requires a partner who understands the intersection of polymer science and textile engineering.
Industrial Sourcing and Design
The bottom line:
- Custom Finishes: Look for suppliers who can apply FR or antimicrobial coatings.
- Volume Capacity: Ensure your partner can handle large-scale industrial roll production.
- Technical Support: Expert sourcing includes consultation on burst strength and elasticity ratings.
Key Takeaway: The most successful industrial projects begin with a consultation to ensure fabric meets all technical specifications.
| Sourcing Factor | Importance | Recommended Action | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Testing | Critical | Request PSI data | |
| Certification | High | Verify FR/ANSI status | |
| Lead Times | Moderate | Plan for custom finishes |
Selecting the right textile is a balance of science and design that determines the ultimate success of your product.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I use apparel mesh for outdoor fencing? No, because it lacks the necessary UV stabilizers for solar exposure.
- Can I print on most polyester mesh? Yes, sublimation printing works exceptionally well on synthetic polyester fibers.
- What’s the best mesh for a humid environment? Synthetic polyester or nylon is best, as they naturally resist mold and mildew.
- What’s the best way to clean mesh fabric? Machine wash cold and air dry to maintain the integrity of the synthetic knit.
- How do I know if my mesh is flame retardant? You must check for a certificate of compliance referencing NFPA 701 standards.
Selecting the right textile is a balance of science and design. Whether you need the high-stretch capabilities of power mesh or the rugged durability of outdoor polyester, understanding these material properties is the first step toward a superior product. To explore our full range of technical textiles or to request a custom solution for your next project, contact us today and speak with a fabric specialist.
Our vision is to provide the global manufacturing industry with the most advanced, durable, and performance-driven mesh textiles available on the market.