Finding the perfect textile for a technical application often feels like searching for a needle in a haystack. For B2B procurement managers and product designers, the wrong choice in mesh or netting can lead to catastrophic product failure, compromised safety standards, and wasted production cycles. Whether you are developing high-performance athletic wear or heavy-duty industrial filters, understanding the nuances of warp-knit structures is essential for maintaining a competitive edge. This complete guide provides the technical insights necessary to navigate the complex world of tulle and mesh fabrics , ensuring your next project is built on a foundation of quality and precision.
What are the foundational types of mesh fabric?
Mesh and netting fabrics are engineered textiles characterized by their open-knit patterns, which create a network of evenly spaced gaps or holes. These materials are designed to prioritize airflow, drainage, and transparency while maintaining high structural integrity. While often grouped together, technical mesh refers to finer structures used in apparel, whereas netting typically describes coarser grids for industrial containment.
Defining the open-knit structure
The primary characteristic of these textiles is the “pore” or hole size.
- Uniformity: High-quality mesh requires perfectly consistent hole spacing to ensure even tension.
- Porosity: This determines the cubic feet per minute (CFM) of airflow allowed through the material.
- Knit Stability: Unlike woven fabrics, these warp-knitted structures do not unravel when cut.
Differentiating mesh from netting
But here is the thing: The difference lies in the application and gauge. Mesh is typically soft to the touch and integrated into garments or fine filters. Netting is often more rigid, utilizing thicker monofilament yarns to withstand heavy loads or environmental abrasion.
Key Takeaway: Foundational mesh structures offer an unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio, providing essential breathability without sacrificing the fabric’s durability.
Summary Table: Mesh vs. Netting Basics
| Feature | Mesh Fabric | Netting Fabric | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pore Size | Fine to Medium | Large to Coarse | |
| Primary Goal | Breathability/Filtration | Visibility/Containment | |
| Structure | Interlocked Warp-Knit | Open-Grid Pattern |
How are different types of mesh fabric manufactured?
The manufacturing process is primarily driven by warp knitting technology, which differs significantly from standard circular knitting or weaving. In warp knitting, the yarns run lengthwise along the fabric, following the “warp” direction. This creates a zigzag pattern that interlocks the loops, resulting in a fabric that is exceptionally resistant to runs and tears, even under high stress.
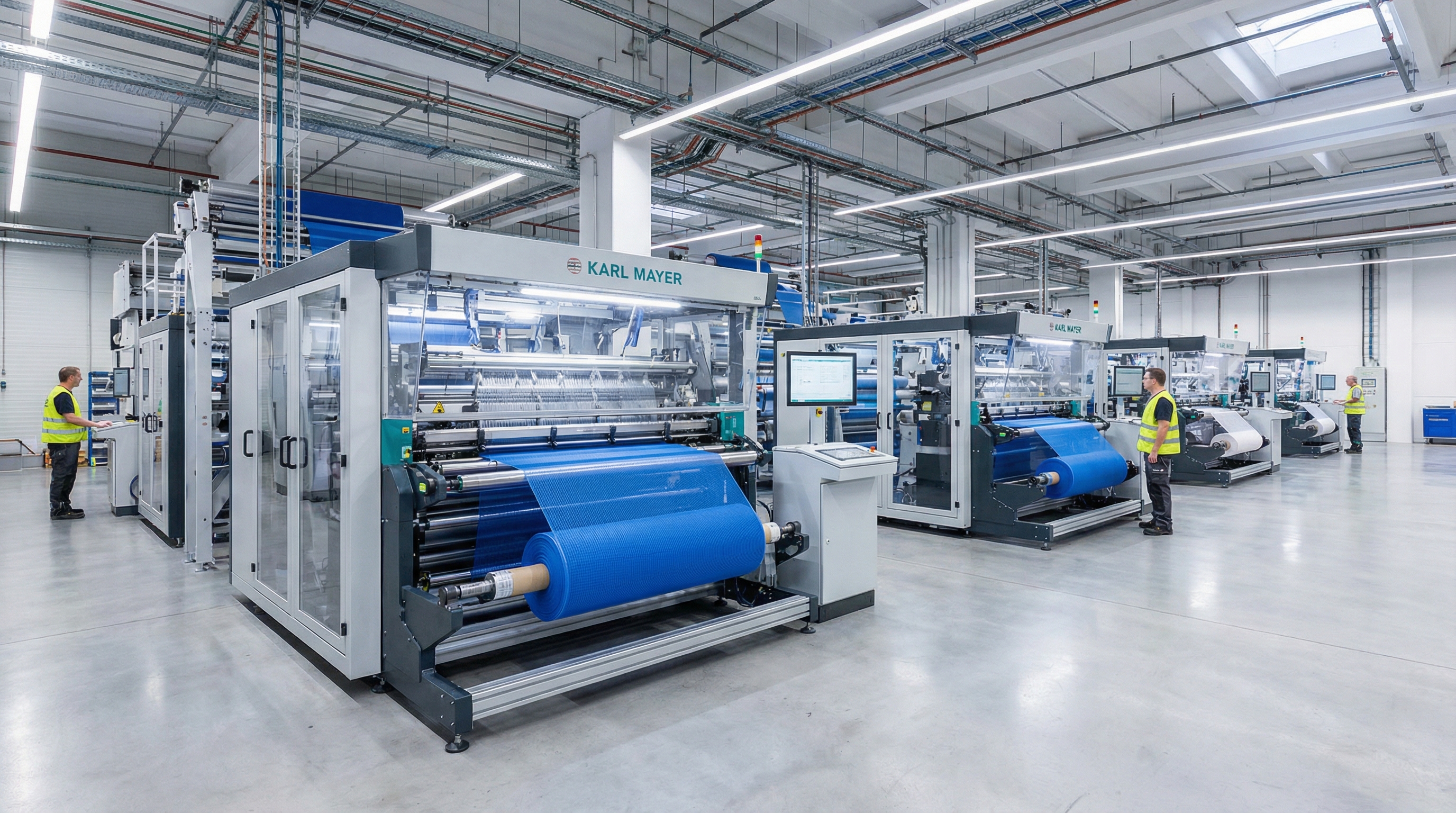

The benefits of Raschel warp knitting
Raschel knitting is the industry standard for creating intricate and heavy-duty patterns.
- Versatility: Allows for various hole shapes including hexagonal, square, and diamond.
- Strength: Can incorporate heavy yarns for industrial-grade filtration or cargo nets.
- Stability: Provides the highest level of dimensional stability in the textile world.
Why Tricot knitting suits finer mesh
Tricot knitting produces a finer, flatter, and softer texture compared to Raschel. It is the preferred method for lightweight apparel linings and delicate tulle , where a smooth hand-feel is just as important as the fabric’s technical performance.
Key Takeaway: The choice between Raschel and Tricot knitting techniques determines the fabric’s ultimate texture, tensile strength, and intended application range.
Summary Table: Knitting Technique Comparison
| Technique | Best For | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raschel | Industrial/Heavy Mesh | Rugged, versatile, coarse | |
| Tricot | Apparel/Lingerie | Soft, fine, lightweight |
Which fibers best support various types of mesh fabric?
The performance of a mesh fabric is fundamentally tied to its polymer base. Polyester and nylon are the two most common synthetic fibers used, each offering distinct advantages depending on the environment. Polyester is generally preferred for outdoor and moisture-rich environments, while nylon is chosen for its superior mechanical strength and elasticity.
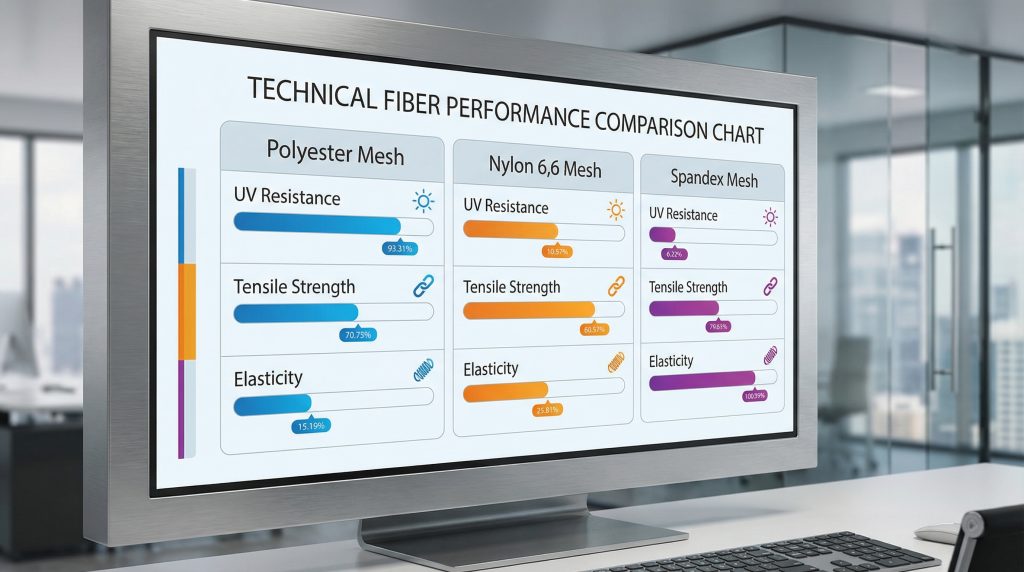
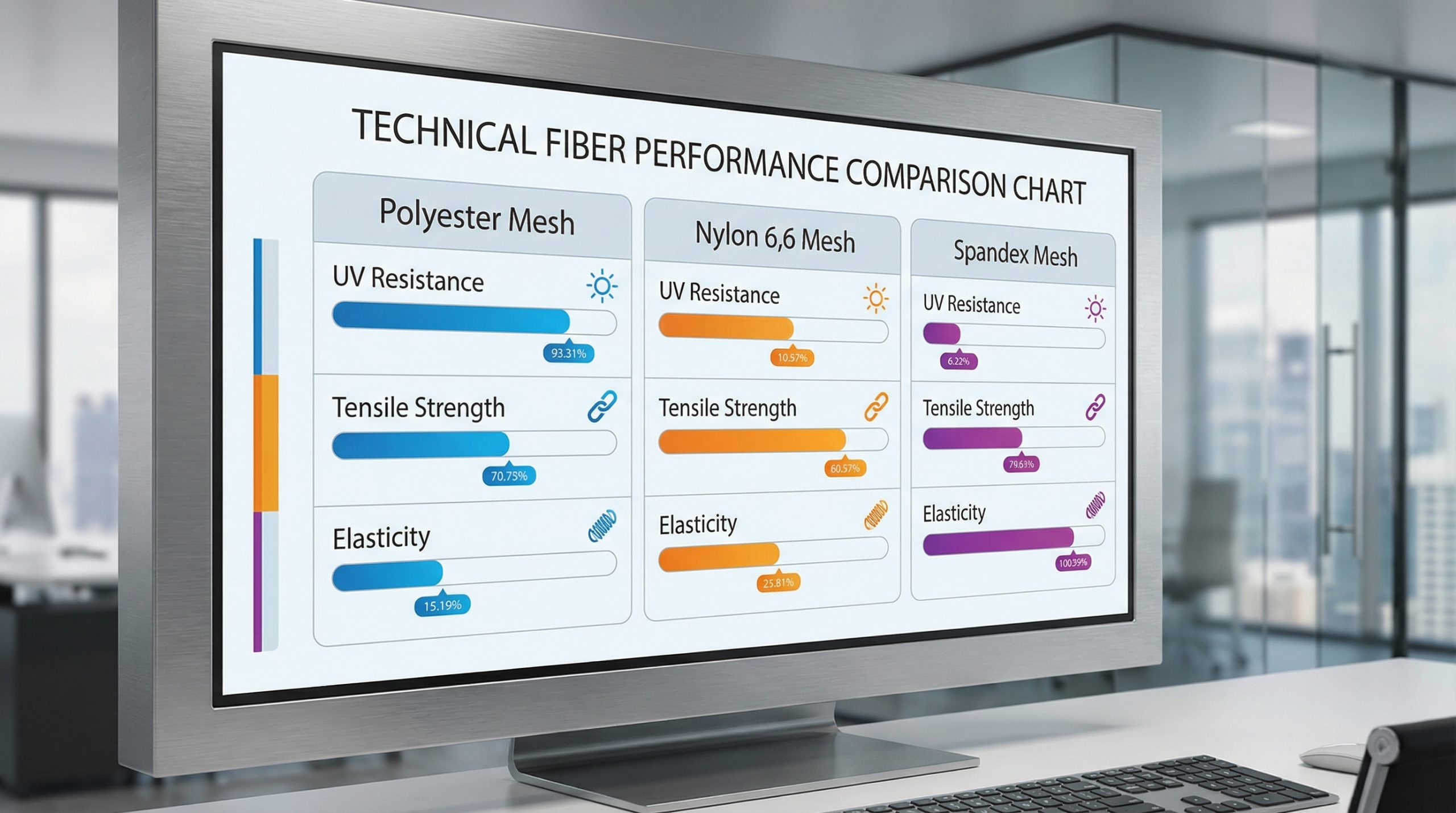
Comparing polyester vs nylon durability
Choosing the right fiber is critical for product longevity.
- Polyester: Naturally hydrophobic and highly resistant to UV degradation, making it ideal for marine and outdoor use.
- Nylon: Offers exceptional abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength, though it can absorb more water than polyester.
The role of spandex in stretch mesh
Think about it. Standard mesh has very little “give.” By integrating elastomeric fibers like spandex (elastane) into the knit, manufacturers create “power” variants that offer significant recovery. This is essential for any application requiring a body-contouring fit or dynamic movement.
Key Takeaway: Selecting the right fiber involves balancing environmental exposure (UV and moisture) against mechanical requirements like tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
Summary Table: Fiber Performance Metrics
| Material | UV Resistance | Tensile Strength | Elasticity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester | High | Medium | Low | |
| Nylon 6,6 | Medium | High | Medium | |
| Spandex Blends | Low | Medium | Very High |
When should you specify high-stretch types of mesh fabric ?
High-stretch mesh, often referred to as power mesh , is a specialized textile engineered for maximum compression and recovery. It is a staple in industries that require structural support without the bulk of traditional solid fabrics. This material uses a unique knit structure that allows it to stretch in four directions while always returning to its original shape.

Understanding four-way stretch dynamics
A fabric that moves with the user is a marvel of engineering.
- Horizontal Stretch: Allows for circumference expansion in garments.
- Vertical Stretch: Ensures length flexibility during movement.
- Compression Power: The force the fabric exerts to provide support to the wearer.
Applications in compression and shapewear
Power mesh is the primary material for post-surgical garments and high-end shapewear. Its open structure ensures that even under high compression, the wearer remains cool. This makes it superior to solid neoprene or heavy elastics in medical and athletic settings.
Key Takeaway: Power mesh is the definitive solution for applications requiring a combination of high elasticity, structural “memory,” and constant airflow.
Summary Table: Power Mesh Applications
| Sector | Application | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical | Surgical Braces | Support and Airflow | |
| Apparel | Shapewear | Compression and Comfort | |
| Lingerie | Bra Wings | Elasticity and Durability |
Why is spacer technology critical for 3D types of mesh fabric?
Spacer mesh is a “3D” textile consisting of two separate fabric layers joined by a vertical microfilament yarn. This internal architecture creates a pressurized air chamber, providing padding and ventilation simultaneously. Because it does not rely on foam, it maintains its shape and breathability even under repeated compression.
The 3D architecture of spacer fabrics
This structure solves the problem of heat entrapment.
- Cushioning: The microfilaments act like millions of tiny springs.
- Moisture Management: Air flows freely through the center, evaporating sweat instantly.
- Thickness Options: Can range from 2mm for apparel to 20mm for industrial seating.
Enhancing airflow in activewear design
By using spacer mesh in footwear and backpack straps, designers can eliminate the need for traditional foam padding. This reduction in weight and increase in breathability is a major selling point for premium performance brands.
Key Takeaway: Spacer mesh serves as a breathable, washable, and significantly more durable alternative to traditional foam padding in technical products.
Summary Table: Spacer Mesh vs. Foam
| Metric | Spacer Mesh | Traditional Foam | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breathability | Excellent | Poor | |
| Washability | Machine Washable | Retains Water/Odors | |
| Weight | Very Light | Moderate |
What performance finishes enhance protective types of mesh fabric ?
Raw mesh can be treated with specialty finishes to meet rigorous safety and performance standards. These chemical or mechanical treatments transform a standard textile into a high-performance tool capable of withstanding extreme conditions or biological threats.

Essential antimicrobial and moisture wicking
In medical and athletic sectors, these finishes are non-negotiable.
- Antimicrobial: Prevents the growth of odor-causing bacteria and mold.
- Wicking: Pulls moisture through the fibers to the surface for rapid evaporation.
- Hydrophobic: Causes water to bead and roll off, keeping the fabric lightweight in rain.
Adding fire retardant and UV protection
For industrial and outdoor use, specialized coatings provide:
- Flame Retardancy (FR): Essential for military and aerospace safety gear.
- UV Inhibitors: Prevent the sun from “rotting” the synthetic fibers over time.
- Soil Release: Allows grease and dirt to be washed out easily in industrial laundries.
Key Takeaway: Performance finishes allow a single base mesh to be adapted for wildly different regulatory environments and specialized safety requirements.
Summary Table: Common Fabric Finishes
| Finish Type | Best Application | Primary Function | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | Medical/Activewear | Odor and Germ Control | |
| FR (Flame Retardant) | Military/Industrial | Fire Safety Compliance | |
| UV Coating | Outdoor Furniture | Prevents Sun Damage |
Where do industrial sectors utilize heavy-duty types of mesh fabric?
Industrial-grade mesh is an indispensable “silent” workhorse in global logistics and manufacturing. These fabrics must meet strict PSI (pounds per square inch) load-supporting requirements to ensure safety. From transport solutions to filtration systems, the strength of the warp-knit structure is tested to its limits every day.

Heavy-duty cargo and transport solutions
Netting is used to secure cargo in trucks, airplanes, and ships.
- Safety: Prevents shifting of heavy loads during transit.
- Weight Reduction: Much lighter than steel or plastic dividers.
- Customization: Can be manufactured with specific burst strengths for aeronautics.
Mesh in automotive and aerospace interiors
In modern vehicles, mesh is used for seat pockets, headliners, and acoustic panels. Because it is lightweight, it helps manufacturers reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, which is a critical factor in increasing fuel efficiency for both electric and combustion engines.
Key Takeaway: Industrial mesh provides essential safety and organization across global logistics while helping manufacturers meet weight-reduction targets.
Summary Table: Industrial Mesh Sectors
| Industry | Specific Use | Property Required | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Seat Pockets | Elasticity/Tear Resistance | |
| Aeronautics | Cargo Dividers | High Tensile Strength | |
| Logistics | Pallet Netting | Low Cost/High Strength |
How do safety-rated types of mesh fabric provide protection?
Protection-grade mesh and netting are engineered to block specific threats, ranging from microscopic insects to falling debris. In these applications, the consistency of the mesh size is not just a quality metric—it is a matter of life and death. Safety-rated fabrics must undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet international standards for impact resistance and aperture size.

Mosquito netting and insect barriers
Fine-gauge mesh is the world’s primary defense against insect-borne diseases.
- Aperture Control: Holes must be small enough to block insects but large enough for airflow.
- Durability: Must resist tearing even after years of use in harsh tropical climates.
- Portability: Lightweight enough to be deployed in field hospitals or emergency shelters.
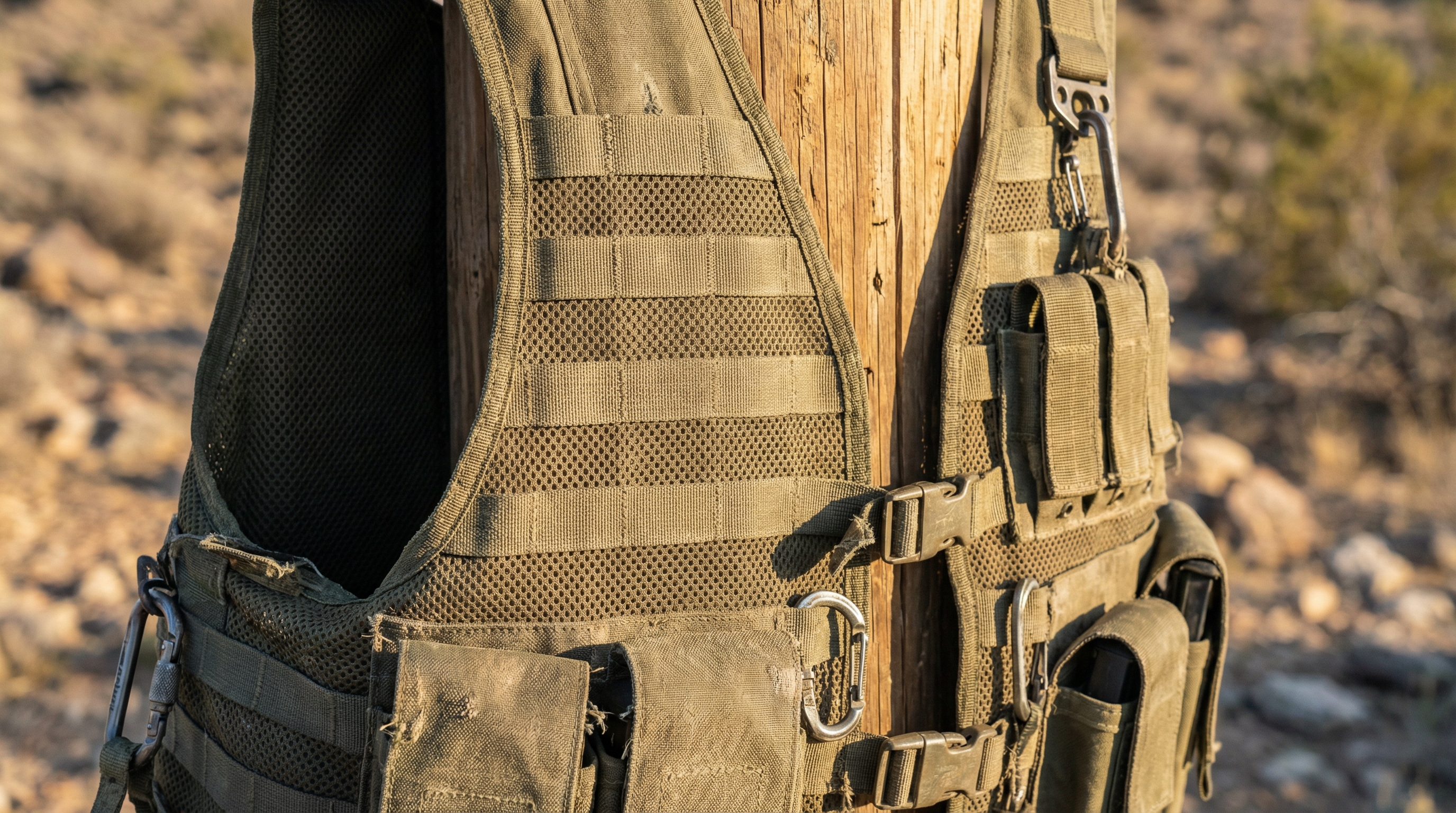
Tactical gear and military-grade netting
Military applications require “MOLLE” (Modular Lightweight Load-carrying Equipment) mesh. This allows soldiers to attach gear to their vests without adding significant weight or bulk. The mesh provides the necessary ventilation to prevent heat exhaustion during high-intensity operations.
Key Takeaway: In safety and defense, the precision of the mesh knit ensures reliable protection against environmental threats and mechanical failure.
Summary Table: Protection Standards
| Application | Threat | Design Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health | Mosquitoes/Insects | High-Density Fine Mesh | |
| Defense | Heat Exhaustion | Lightweight Warp-Knit | |
| Safety | Falling Debris | High-Impact Construction Mesh |
Are there sustainable options for modern types of mesh fabric?
The textile industry is rapidly transitioning toward “circularity.” Many B2B suppliers now offer mesh made from Post-Consumer Recycled (PCR) polyester, often sourced from ocean-bound plastic bottles. These sustainable options allow brands to reduce their carbon footprint without sacrificing the mechanical performance of the textile.

Transitioning to recycled polyester fibers
The move to recycled content is a major trend in B2B procurement.
- Resource Savings: Using PCR polyester significantly reduces energy and water consumption.
- Waste Reduction: diverts plastic waste from landfills and oceans into high-value products.
- Performance Parity: Modern recycled fibers offer the same strength and durability as virgin polyester.
The lifecycle of eco-friendly synthetics
Sustainable mesh isn’t just about the raw material; it’s about longevity. High-quality warp-knit mesh is designed to last for years, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing the overall textile waste generated by a product’s lifecycle.
Key Takeaway: Eco-friendly mesh options allow businesses to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals while maintaining high product performance.
Summary Table: Sustainability Metrics
| Material Source | Energy Savings | CO2 Reduction | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin Polyester | 0% (Baseline) | 0% (Baseline) | |
| Recycled Polyester | ~45% | ~30% |
Can you request custom parameters for specific types of mesh fabric ?
Off-the-shelf fabrics rarely meet the exact needs of innovative new products. Customization allows engineers to specify the exact diameter and shape of the mesh openings to optimize airflow, filtration, or aesthetic appeal. Whether you need a specific weight or a unique color match, custom manufacturing is the key to product differentiation.

Developing bespoke hole sizes and patterns
Here’s the kicker: A slight change in hole geometry can completely change a product’s performance.
- Hexagonal Patterns: Offer the best multi-directional strength.
- Square/Diamond Patterns: Often preferred for aesthetic or traditional netting looks.
- Variable Density: Creating “zones” of different mesh densities within a single fabric roll.
Achieving precise weight and tensile strength
Whether you need a mesh that weighs 2 ounces per square yard for garment lining or 20 ounces for heavy-duty industrial screens, custom manufacturing ensures the fabric meets the specific load-bearing requirements of your project.
Key Takeaway: Customization is the ultimate tool for product designers looking to optimize technical performance and achieve a unique brand identity.
Summary Table: Customization Options
| Variable | Range of Options | Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hole Shape | Hex, Square, Diamond | Aesthetics/Airflow | |
| Fabric Weight | Ultra-light to Heavy | Durability/Cost | |
| Color | Custom Dye-Matching | Brand Identity |
Navigating the specifications of mesh and netting requires a deep understanding of fibers, knitting techniques, and performance finishes. By focusing on the structural integrity of warp-knit designs and the versatility of modern synthetics, businesses can develop products that are both innovative and reliable. When you are ready to source high-quality, factory-direct materials for your next project, explore the extensive catalog and custom development services available at TulleMesh . From apparel to industrial protection, the right mesh makes all the difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between polyester and nylon mesh?Polyester mesh is superior for UV resistance and moisture-wicking, making it the choice for outdoor use. Nylon mesh offers higher abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it better for high-stress industrial applications.
2. Is mesh fabric waterproof?By nature, mesh is an open structure and cannot be waterproof. However, it can be treated with hydrophobic (DWR) finishes to make the fibers shed water, and it is often used in “water-friendly” products because it drains and dries extremely quickly.
3. Can power mesh be used for medical applications?Yes, power mesh is widely used in medical braces, compression sleeves, and post-surgical garments because it provides stable support while allowing the skin to breathe.
4. What does “warp-knit” mean in mesh production?Warp-knit refers to a manufacturing process where yarns run vertically. This creates a loop structure that is “run-proof,” meaning if the fabric is punctured, the hole will not expand or unravel like a standard knit.
5. How do I choose the right hole size for my product?Hole size (aperture) should be chosen based on the required airflow and what you need to filter or contain. Smaller holes offer more privacy and finer filtration, while larger holes provide maximum breathability and visibility.